Edited by:
Marco Cordani, PhD, Complutense University of Madrid, Spain
Ilaria Dando, PhD, University of Verona, Italy
Giulia Ambrosini, PhD, University of Verona, Italy
Pedro González-Menéndez, PhD, University of Oviedo, Spain
Submission Status: Closed
This collection is no longer accepting submissions.
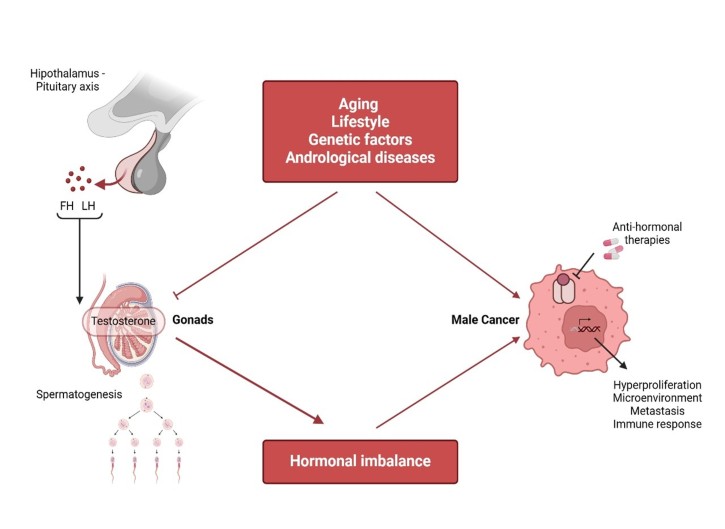
Cell Communication and Signaling is calling for submissions to our Collection on Mechanisms and Etiology of Male Health Disorders: Hormones, Cancer, and Fertility. We invite papers that elucidate novel cell signaling pathways and mechanisms of action, as well as papers that address therapeutic strategies that target disease processes.